
Degradation due to nonlinear effect can be minimized by using appropriate dispersion compensation schemes.

SPM affects the optical signal by its interaction with pulses broaden due to dispersion. Single channel transmission is affected by SPM only whereas multi channel transmission has combined effects of SPM, XPM, and FWM which lead to signal degradation. The nonlinear effects included in the NLSE are self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), and four-wave mixing (FWM). (1) can be neglected on such condition, and if the reference time frame moves with pulse at the group velocity, v g i.e. For pulses of width T o > 5 pico-second, the parameters 1/( ω ο To) and T R/T 0 become so small (< 0:001) that the last two terms in eqn. (1) are related to the effects of self-steeping and stimulated Raman scattering, respectively. The last two terms in the right side of the eqn. The term proportional to θ 3 account for third-order dispersion, and only becomes important for ultra short pulses, because of their wide bandwidth. Where A represents the optical field envelope, γ is the nonlinearity coefficient, α is the attenuation constants θ 1, θ 2 and θ 3 are first-order, second- and third-order derivations of the propagation constant θ about the center frequency ω ο and they are related to the dispersion of the optical fiber, and T R can be related to the slope of the Raman gain spectrum and is usually estimated to be 3 femto-second at wavelengths near 1550 nm. Effect of fiber nonlinearity on long-distance transmission. San Diego, CA: Academic 1995., 10 Marcuse D, Chraply AR, Tach RW. It describes the evolution of optical field at the transmission distance z as [ 9 Agrawal GP. This paper is divided into V sections: Section II consists of theory, Section III deals with the system description including description of system parameters, Section IV shows the results & discussion and finally Section V concludes the paper.Īvoiding polarization and scattering effects such as stimulated Raman scattering and stimulated Brillouin scattering, propagation of optical pulses in fiber is described by the scalar nonlinear Schrodinger’s equation (NLSE).

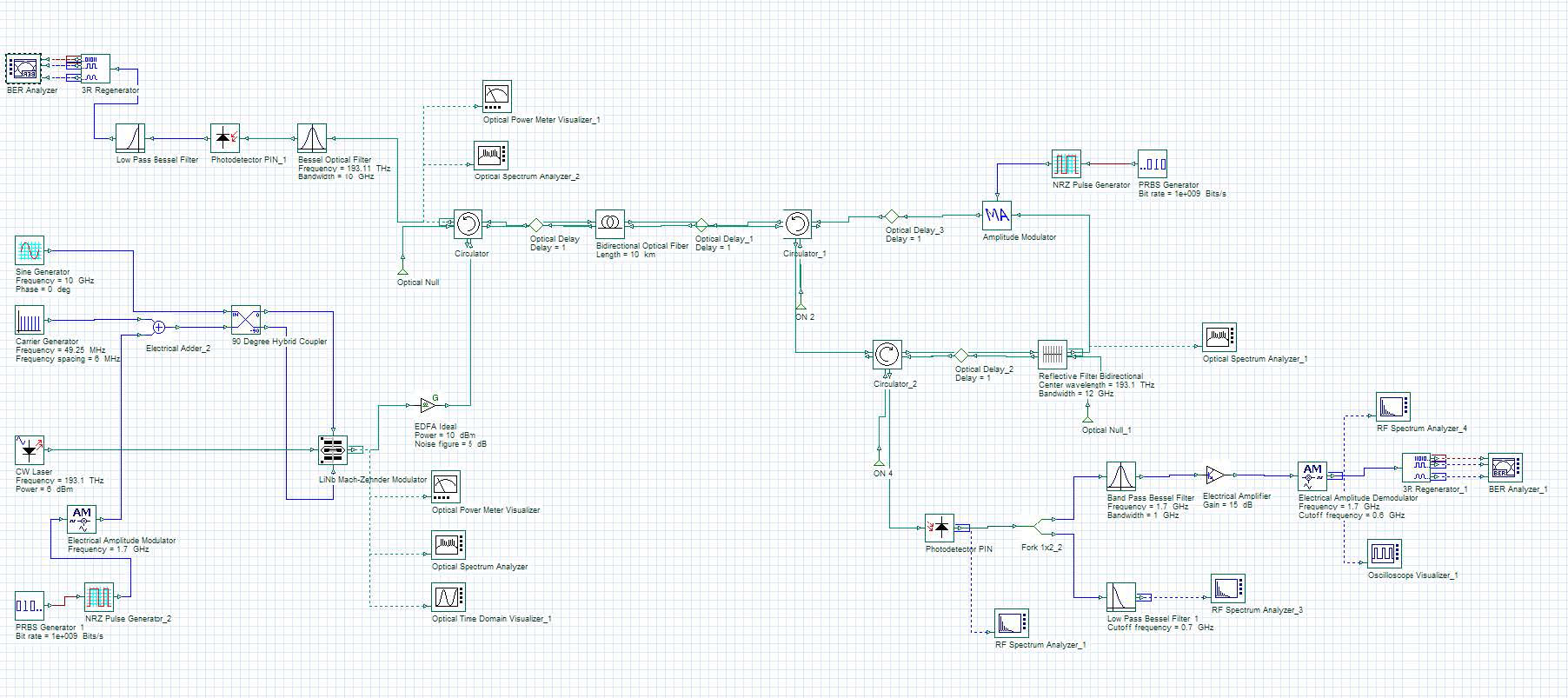
The network layout is designed and simulated with the help of Optisystem 7 software. In this paper the performance of the system is measured in terms of Q factor, BER and Eye Diagram by varying the system parameters. presented the characterization of fiber Bragg grating for dispersion compensation. presented the group velocity dispersion (GVD) and nonlinear effects, such as self- and cross-phase modulation (SPM/XPM) and four-wave mixing (FWM) in wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) systems at 10 Gb/s that degrade the performance of the system. analyzed Fibres-optic dispersion and its effect on optical transmission system. shows optimization of dispersion compensating fiber for long haul applications. A novel design of a dispersion compensating fiber. presented a novel design of a dispersion compensating fiber [ 4 Thyagarajan K, Varshney RK, Palai P, Ghatak AK, Goyal IC.
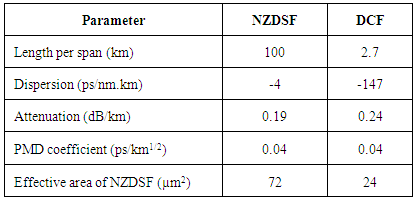
Fiber-Optic Communications Systems, 3 rd ed. Several dispersion compensation techniques available are- Dispersion shifted fibers, Dispersion-flattened fibers, all pass filters, raised cosine filter, high order mode fibers, DCF’s & Fiber Bragg Grating etc. Thus, it is necessary to find out an effective dispersion compensation technique that leads to performance enhancement of the optical system. Due to this overlapping the output becomes undetectable. Dispersion causes broadening of pulses which leads to Inter-Symbol-Interference (ISI), in which the output pulses of a system overlaps. ĭispersion can be defined as broadening of light pulses in an optical fiber which decreases the data rates, signal to noise ratio and quality of the system. Amongst them dispersion effect is dominant and is difficult to overcome in comparison of other problems. Like other communication systems, optical communication system also faces problems such as dispersion, attenuation and non-linear effects that degrade its performance. The light is an electromagnetic carrier wave, which is modulated to carry information. Information in fiber optic communication system is transmitted in the form of light pulses from transmitter to receiver.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
